As summer has worn on there have been a growing number of headlines focused on Toronto’s stagnant condo market. In short, the number of units for sale continues to grow as buyers refuse to pay the elevated prices being demanded by sellers. Interestingly sale activity has been stagnant and prices haven’t really moved despite the growing inventory.

The knock on effect has been a significant slow down in new developments. This has led to growing concern that prices will rise in the future as new supply is postponed or canceled, and pressure is growing to get interest rates lowered to help stimulate buyers.
All of this sounds a touch too convenient for me. One of the reasons (not the only reason, but a significant one) we face a “cost of living crisis” is that housing has increasingly been seen as an investment, one that people have had greater faith in than other traditional assets. But housing booms aren’t new, and it seems odd to me that our chief concern about a growing glut of over-priced condos will be that condo prices will be higher in five to ten years. A more pressing concern is likely that condo investors, and the banks that have provided the mortgages, are deeply concerned that if buying doesn’t resume property prices could take a serious decline, erasing Canadian wealth and forcing Canadian banks to write down balance sheets.
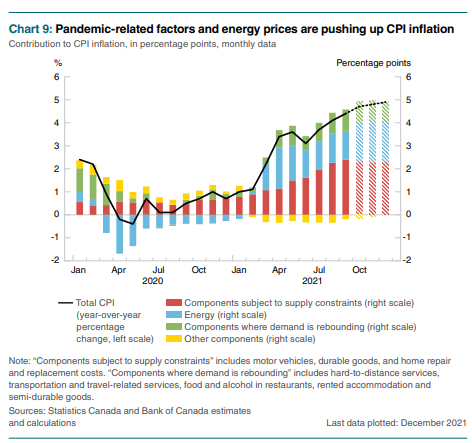
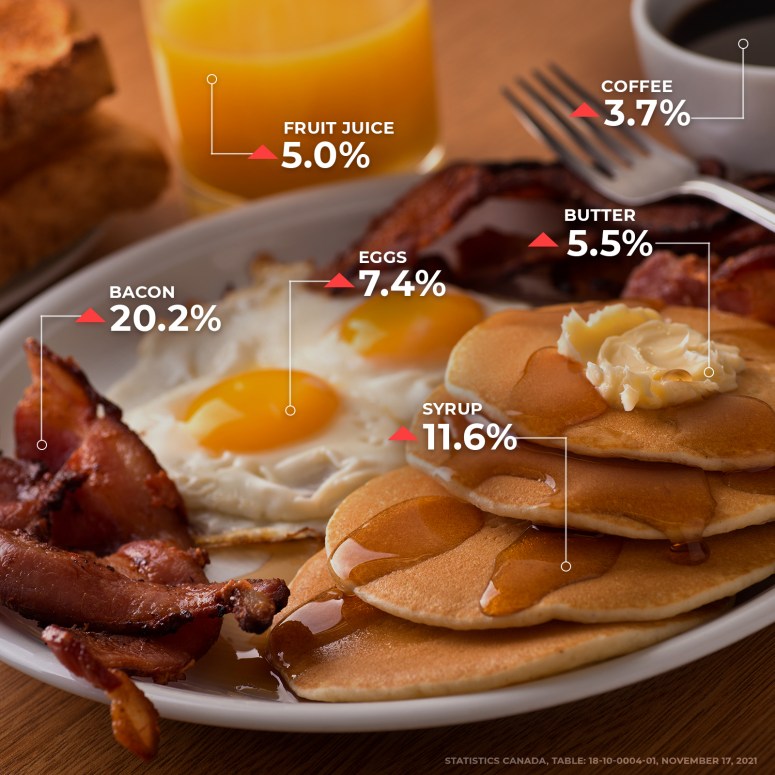
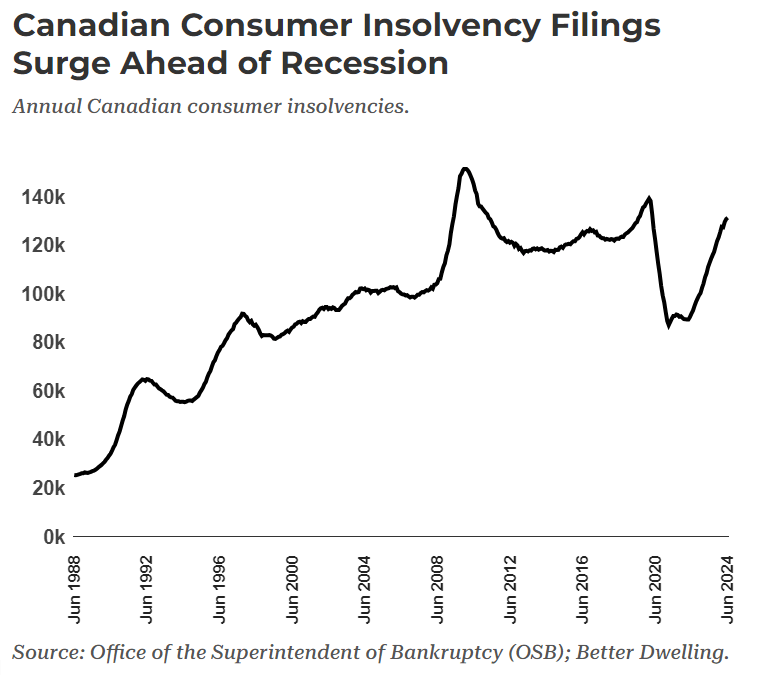
For many this would be a welcome relief, potentially opening Toronto’s property ladder and easing some of the burden of the cost of living. But property ownership has been the source of growth of Canadian wealth over the past twelve years. According to Credit Suisse, Canadian wealth rose by two thirds from 2010 to 2022, however Canadian economic growth was quite weak, with income only rising by 15% over the same period. In other words, if Canadians are richer today than they’ve been in the past, its because they owned homes, not because the economy was paying more. Independently, we might conclude that there was something unique happening with Toronto’s condo market, but this news goes hand in hand with other worrying economic trends in the country. Notably, Canadian consumer insolvencies have been steadily climbing while unemployment has also been climbing. The unsold condo inventory is the highest it’s been since 2008, while data shows that household credit growth has been decelerating. Other disturbing news includes the expansion of the public sector, which now accounts for 1 in every 4 employed Canadians while public sector growth accounted for 49% of our most recent GDP growth.


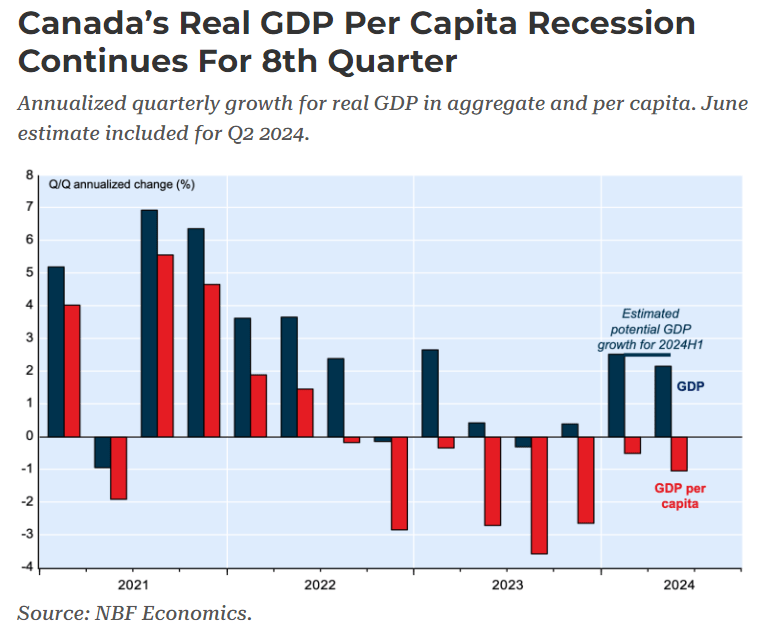
2024 has been a disappointing year for Canadian economic news. Aside from the headlines above, one of the most striking statistics is that Canada is losing economic ground per capita. Much of our GDP growth is coming from high immigration, in effect importing new economic activity but at a rate below what is needed to expand the economy on a per person basis, and it has been doing so for more than 2 years. We are, in effect, in a “per capita recession”.
Since 2022, interest rate increases have pummeled the economy, particularly real estate, which has grabbed a lot of headlines. But Canada’s real estate market has shown considerable resilience through the first few years. However, investors that over are extended and feel the building pain from higher borrowing costs are starting to exit their investments. That hasn’t been altered by the recent interest rate cut which has yet to stimulate much new buying activity. Pressure is building from sectors of the economy to see rates fall and hopefully ease or reverse the effects of higher borrowing costs, but it remains to be seen whether rate cuts can happen at a pace both responsibly and fast enough to substantially change the direction of Canada’s economy (if it can at all).
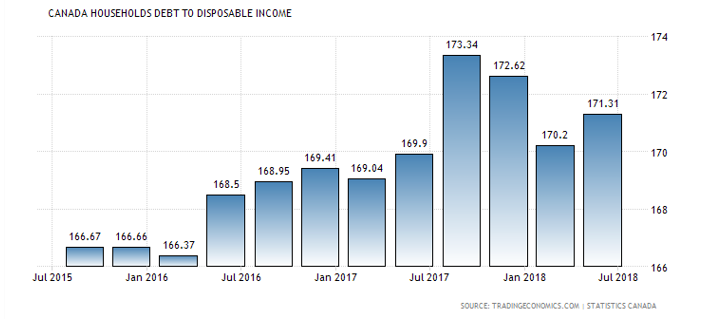
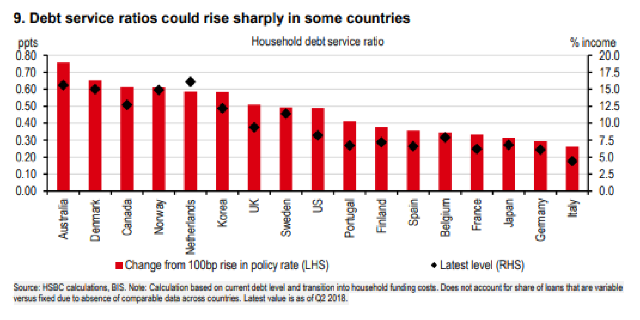
On Monday, August 5th, changes in interest rates from the Bank of Japan reportedly triggered an unwinding of a popular “carry trade”, in which large institutions borrowed money in Japan for low cost, and then invested that money in US stocks. A hike in the BoJ’s lending rate had forced up the value of the yen, forcing the sale of those same US investments to pay back the now more expensive Japanese loans. Markets have recovered quickly, but it shook investor confidence, and while the explanation may not be wholly accurate, it’s a useful reminder that debt, which offers real value when used in moderation, can make economies extremely fragile. For years Canada has had the highest level of household debt to disposable income of any G7 country, and much of that was tied up in housing. What happens next is anybody’s guess.


Aligned Capital Partners Inc. (“ACPI”) is a full-service investment dealer and a member of the Canadian Investor Protection Fund (“CIPF”) and the Canadian Investment Regulatory Organization (“CIRO”). Investment services are provided through Walker Welath Management, an approved trade name of ACPI. Only investment-related products and services are offered through ACPI/Walker Wealth Management and covered by the CIPF. Financial planning services are provided through Walker Wealth Management. Walker Wealth Management is an independent company seperate and distinct from ACPI/Walker Wealth Management.