To many Canadians the CPP is something that you simply receive when you turn 65, (or 70, or 60, depending on when you want or need it) with little consideration for how the program works or is run. That’s too bad because the CPP is successful, enlightening and puts its American counterpart, Social Security, to shame.
To many Canadians the CPP is something that you simply receive when you turn 65, (or 70, or 60, depending on when you want or need it) with little consideration for how the program works or is run. That’s too bad because the CPP is successful, enlightening and puts its American counterpart, Social Security, to shame.
You’ve probably heard American politicians decrying the state of Social Security, claiming that it is broken and will one day run out of money. That’s a frightening prospect for those who will depend on it in the future. Social Security is a trust that buys US debt, and its use of US Treasuries (low risk debt issued by the US government) is crippling that program and even puts it at odds with attempts to improve government financial health (it’s more complicated than this, but it’s a useful guide). In comparison the CPP isn’t bound by the same restrictions, and operates as a sovereign wealth fund.
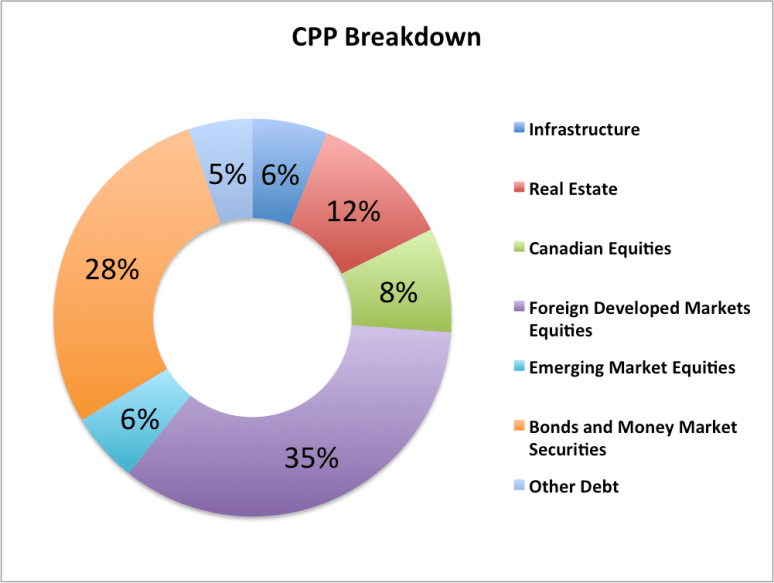
A sovereign wealth fund is simply a fancy way to describe a program that can buy assets, which is exactly what the CPP does. The Canada Pension Plan may be larger and more elaborate than your RRSP, but it can look very similar. The CPP has exposure to Canadian, American, European and Emerging Market equity. It invests in fixed income both domestically and abroad, and while it may also participate in private equity deals (like when the CPP bought Neiman Marcus) in essence the investments in the CPP are aiming to do exactly what your RRSP does.
The big lesson here is really about risk though. The CPP is one of the 10 largest pension plans in the world. It’s wildly successful and is run in such a way as to be sustainable for the next 75 years. The same cannot be said for Social Security. But by taking the “safest” option Social Security is failing in its job and will run out of money by 2033. But by buying real assets and investing sensibly the CPP is far more likely to survive and continue to thrive through all of our lifetimes.
What’s also notable is what the CPP isn’t trying to do. It isn’t concentrated in Canada. It doesn’t need to get a substantial rate of return, and it doesn’t need every sector to outperform. It needs consistent returns to realize its goals, and that’s how it’s positioned. By being diversified and not trying to time the market, the CPP finds success for all Canadian investors.
I’ve said in conversation that if there was an opportunity to invest directly in the CPP I would take it. However until then the best thing investors can do is take the CPPs lessons to heart!